TDS on Property – Section 194IA of Income Tax Act, 1961
Written by
:Reviewed by
What is Property Tax?

Property Tax, also known as House Tax, is the tax levied on real estate owners by the authorities such as a municipality or municipal corporation. It is used for maintenance and running of the local public amenities of the area, such as roads, sewage system, parks, lighting, and other infrastructure services.
It is levied usually on all real estate properties, including buildings whether residential or commercial, attached land, and improvements made to the property, but not on vacant plots of land with no adjoining building.
These taxes usually calculated on the value of the property owned as well as the land.
The different property divisions include:
1. Land – in its most secure form, without any construction or upgrading.
2. Improvements made to land - this includes immovable manmade creations like buildings and go downs.
3. Personal property – This includes movable manmade objects like cranes, cars, or buses.
4. Intangible property
Calculate your Income Tax
Overall Summary
- 100% Guaranteed returns*#
- Save tax up to Rs. 46,800##
What is Section 194IA of The IT Act?
a) TDS on property, as the name implies, is a tax deducted at the source on guaranteed income received by a person
b) TDS on property is usually deductible from the remitter of the income and deposited with the Income Tax Department
c) In Section 194IA and Section 194IB, TDS on property is deducted by the buyer of property and payer of the rent, respectively
d) TDS on property can be claimed at the time of filing your Income Tax Returns
e) Section 194IA prescribes that a buyer of immovable property that costs more than Rs.50 lakhs is required to deduct TDS on property while paying the seller. The rate of TDS on property for this deduction is 1%.

Requirements of Section 194IA
1) TDS on property is to be deducted by the buyer and not the seller.
2) There are no TDS applicable under Section 194IA if the transaction is worth less than Rs.50 lakh.
3) TDS on property must be paid on the full amount of sale and not only the sum above Rs.50 lakh. For instance, if you buy a property with a value Rs.70 lakhs, TDS will be calculated on Rs.70 lakh and not Rs.20 lakh.
4) For payment made in instalments, TDS will be deducted on each instalment.
5) Since September 2019, payments such as club membership, car parking, advance fees, maintenance fees, electricity fees have also been comprised under 'consideration for immovable property'. It implies that such charges attached to the property will also be included in the taxable total.
6) PAN cards of both buyer and seller are mandatory for TDS on property deduction under Section 194IA.
7) If the buyer does not obtain the seller's PAN, the rate of TDS rises to 20%.
8) The TDS on the immovable property must be paid using Form 26QB in 30 days from the end of the month when the TDS was deducted.
9) The buyer is required to obtain Form 16B and issues the form to the seller.
TDS on Purchase of Property

a)To keep a check on the extensive use of black money in immovable property transactions, the government of India has introduced a law, where the purchaser of a property has to deduct tax at source, i.e. TDS on property while paying the seller for his property.
b)Under Section 194IA of Income Tax Act, a buyer is required to deduct TDS at the rate of 1% of the sale consideration. This is applicable if the value of the payment is Rs.50 lakh or more.
c) The Section covers residential property, commercial property, as well as land. You must note that transactions relating to the purchase of agricultural land are not covered under this provision.
Now the question arises when to deduct the TDS on property purchase? The purchaser is required to deduct TDS on property at the time of crediting the amount to seller’s account or time of payment, whichever is earlier.
How to Claim TDS on Sale of Property?
a) From 1 June 2013, when a buyer buys immovable property (i.e. a building or part of a building or any land except agricultural land) costing more than Rs.50 lakh, he must deduct tax at source (TDS) when he pays the seller.
b) This has been laid out in Section 194IA of the Income Tax Act.
c) The buyer obtains Form 16B and issues the form to the seller.
The property seller has to do the following:
1) Provide PAN to the buyer who in turn will fill-up the form online and submit to the Income Tax Department for TDS.
2) Verify that the property buyer has deposited the taxes deducted from sale consideration and should be reflecting in the Form 26AS Annual Tax Statement.
3) Get the Form16B for paying the TDS.
How to File TDS on Property (Form 26QB)?
Step 1: Log on to the website: https://onlineservices.tin.egov-nsdl.com/etaxnew/tdsnontds.jsp
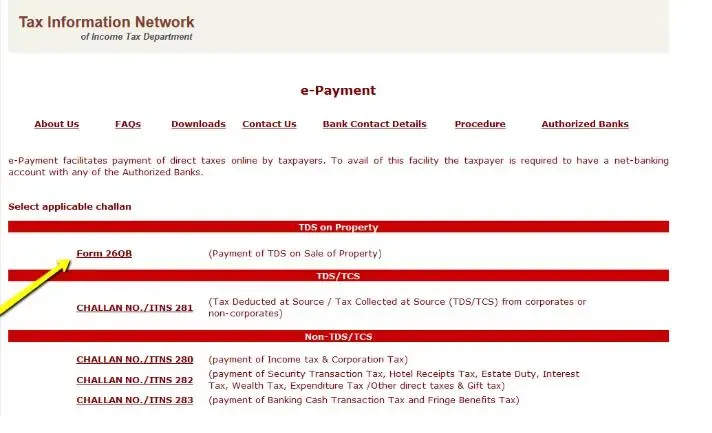
Step 3: Select "TDS on sale of property" as the applicable challan.
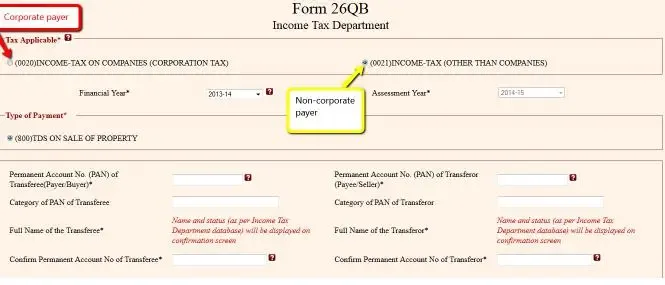
Step 4: The following information is needed to fill the form:
1. PAN of both buyer and seller
2. Details of the property
3. Seller's residential address
4. Contact detail of both buyer and seller
5. Tax deposited and the amount credited
Step 5: After filling the form mentioned above and submitting it, you will get a confirmation. You can print the form for future acknowledgement.
Step 6: If you want to make an online payment, then proceed to "Submit to the bank" and make the payment through reliable net banking facility.
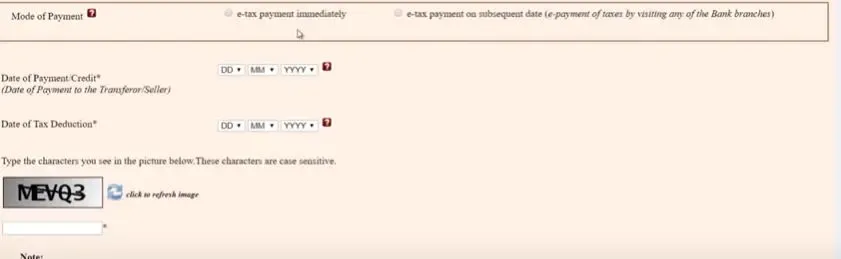
Step 7: Once you are through with the payment, there will be a display of a TDS challan demonstrating CIN, name of the bank through which online payment is made with all the payment details.
Penalties Applicable on Non-Filing of TDS
a) The tax amount deductible must be paid to the government within seven days of any such transaction made.
b) The penalty of not paying TDS on property can go up to Rs. 1 lakh under Section 271H.
c) To avoid any type of penalty, you must pay the TDS on property along with interest amount and any late payment fee as and when you receive a tax notice.
d) Under Section 201, you will have to pay an interest of 1% per month if the tax was not deducted at all.
e) 1.5% interest will have to be paid if the tax was deducted but not deposited with the government.
f) In case of default on account of non/late filing of Form 26QB, a fee shall be levied u/s 234E of the Act.
g) The late filing fee applicable under Section 234E is Rs. 200 per day dependent on the maximum tax due.
h) If the property seller has already paid capital gains tax, the late filing fee could be reduced or cut off altogether.
However, to avoid getting into such penalties, it is advisable to stay on track and pay all taxes on time.
TDS on Property Rent
a) Section 194IB of the Income Tax Act is associated to the TDS on property rent. The Section is primarily for the people who are earning from renting or leasing their property.
b) The rent receivable on property is subject to TDS on property as it is an additional income earned by individuals like salaried people or businessmen.
When to deduct the TDS on Property Rent?
b) Both individuals and members of Hindu Undivided Family are obligated to TDS of property at 5% of the rent collected given the rent exceeds Rs.50,000 per month.

More plans for you
FAQs About TDS on Property
ARN NO: Aug23/Bg/05M
Save 46800 on taxes if the insurance premium amount is Rs.1.5 lakh per annum and you are:
- Regular Individual
- Fall under 30% income tax slab having taxable income less than Rs. 50 lakh
- Opt for Old tax regime

Secure your family against unexpected situations with Max Life Insurance
99.65% Death Claim Paid Ratio^
Financial protection throughout life
Popular Searches
- 0124 648 8900(09:00 AM to 09:00 PM Monday to Saturday)
- service.helpdesk@maxlifeinsurance.comEmail
- SMS ‘LIFE’ to 5616188Message
- Let us call you back
- 1860 120 5577(9:00 AM to 6:00 PM Monday to Saturday)
- Chat with us
- Write to usPlease write to us incase of any escalation/feedback/queries.
- 011-71025900, 011-61329950(9:00 AM to 6:00 PM Monday to Saturday)
- nri.helpdesk@maxlifeinsurance.comPlease write to us incase of any escalation/feedback/queries.




